- Home
- Getting started
- Website guide
- Backgammon school
- Lobby
- Tournaments
- Tell a Friend
- News
GAME LOBBY

Enter a free room from the list, choose an available player as opponent or create a game with your own rules.
Go to Lobby
FAQ

You can easily find an answer in the list of frequently asked questions by the users in no time.
Check the FAQs
TELL A FRIEND

Invite your friends to play backgammon at UltimateRoll and get a bonus of $100 for every friend who registers.
Invite your friends now
GETTING STARTED

Easy guideline through the essential steps, beginning with registration at UltimateRoll, activation and playing the game.
Begin now
WEBSITE GUIDE

If you are totally new to the game of backgammon or even want to learn all of the rules and strategies, read on.
More on Website Guide
Backgammon history
Backgammon is one of the oldest games in the history of mankind, alongside Go and Chess. The exact origins of the backgammon remain unknown, but it is believed all around the world that the game originated probably about 5000 years ago in ancient Mesopotamia (today's Iran, Iraq and Syria). In the early beginnings, this game was played more or less in the same way as today, on a wooden board or a table. Back then, the equipment kit consisted of stones or small rocks used as checkers and a numbered dice made from either wood, pottery, stones or bones. Throughout the history, the game of backgammon has usually been associated with nobles and royal people. Among many backgammon artifacts found up to date, some of them clearly proof the popularity of this game among the aristocrats and even rulers in Southeast Europe as well as the Middle and the Far East. According to many findings, the Roman Game of twelve lines (Ludus Duodecim Scriptorum) is probably the ancient game most similar to the modern backgammon. In Roman time the Emperor Nero who was a prodigious gambler also enjoyed playing backgammon. He even played for today's equivalent of $15,000 a game. On the other hand, another Emperor, Claudius known as a keen player, had a special board build on the back of his chariot for making his boring journeys more fun and pleasurable.
But the aristocracy was not the only party who enjoyed the fun of the backgammon. The popularity of the game also spread between the ordinary people too. At Pompeii a fascinating wall painting was found portraying a backgammon tale in two scenes. In the first one, two players are arguing over a game in progress, while the second one depicts an innkeeper throwing the two fighting opponents out of his establishment. Around the 11th century this game is not just popular in the Middle East, but also in whole Europe. Although Queen Elizabeth even prohibited the backgammon completely, the habit and enjoyment for playing the game had never been lost between the ordinary people.
The game of backgammon throughout the centuries, in different countries evolved differently, but the concept and the basics of the game remain the same. There are also many other similar games or variants of the standard backgammon game that are played in many countries, which are actually modification of the original one.
Rules & setup
Backgammon is a game of skills, tactics, luck and intuition, a game where two players compete against each other. Despite the vagaries of the dice, usually the more experienced and knowledgeable player wins in the long run. Many people think of backgammon as a gambling game, because of the use of dice, but opposite to the other games, a single game or a match can also be won with great skills and not so fortunate dice. However, due to the luck element of the dice involved in the game, sometimes an absolute beginner can win over a real experienced champion. In many situations the outcome of the game is often uncertain until the very last rolls of the dice, when it can all fall apart for one player and exactly the opposite for the other. Therefore, the luck is definitely involved and has a huge impact on the final result, but the most important thing is the usage of good tactics when moving the checkers across the board.
In backgammon the line between winning and losing is very slim, since many players lose a game from a previously winning position, because of the lack of knowledge about closing games. For that reason, having a good strategy that involves always making blocked points, prime, not leaving blots on the board, hitting or blocking the opponent’s checkers as much as possible, can very easily influence the game with a positive final outcome.
On the board there are twenty-four narrow triangles that are grouped into four quadrants of six triangles each. These triangles are called points and are used as positions for the checkers. Before the game starts, the checkers are placed in their initial starting position for the game. Throughout the game these checkers move between different points according to the roll of the dice. The player who bears off the checkers first is the winner of the game and wins the original stake or even more, depending on the position of the opponent’s checkers.
The points on the board are numbered for each player, starting count from the player’s home board. The first point is number one, whereas the final outermost is number twenty-four. The last twenty-four point is actually the opponent’s point number one that resides in opponent’s home board. Between the player’s home board and the outer board there is a bar which is used for placing checkers hit by the opponent.
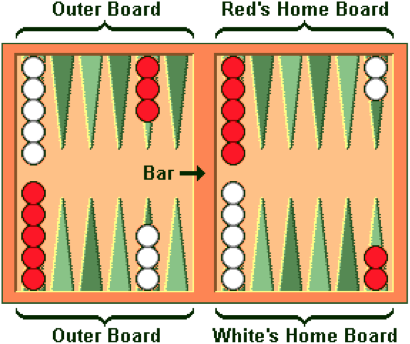
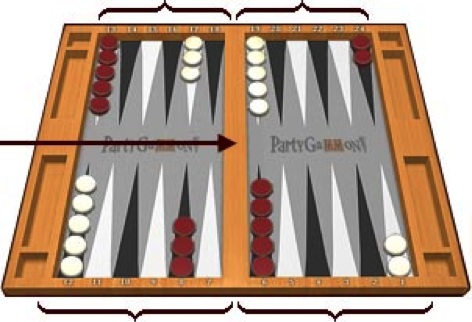
Thirty checkers in total are used by the players, fifteen white and fifteen black. Before the game starts, each player chooses which checker color is going to use for the game. The initial arrangement of the checkers for each player is:
- two checkers placed on point twenty-four,
- five checkers placed on point thirteen,
- three checkers placed on point eight,
- five checkers placed on point six.
A doubling cube, with numbers 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 on each face, is used to keep track of the current stake of the game, but is optional and is negotiable before the start of the game between the players if it is going to be used or not during the game. This special die is used to change the original stake negotiated prior to the game. When the doubling cube has number different than number 1, then the new stake has the value of the original stake multiplied by the number of the doubling cube.
Object of the game
The main goal in backgammon is moving all the checkers around the board into the home quadrant and bearing them off. The player who bears off the checkers first wins the game. From the position of the opponent’s left checkers on the board depends the type of the win, which can be a normal, gammon or a backgammon.
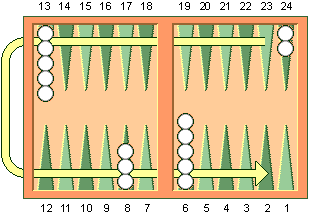

Movement: Before the game starts, each of the two players roll a die and player with the higher number starts first. This player then rolls the dice again in order to begin his/hers turn, instead of using the dice numbers of the initial roll. This is a case where only a single game of backgammon is played. It does not apply for a match play, in which case the player that won the previous game, automatically has the first turn in the next one. When both players have the same number of the die, they roll again and this step is repeated as many times needed until they roll different numbers. When a player finishes the turn by playing the checkers according to the dice numbers, then it is the opponent’s turn. Finally, if a player does not have an available move for any of the numbers of the dice or both, then the player’s turn ends, and the opponent’s turn starts.
The roll of the dice indicates how many points the player can progress by moving the checkers towards the home board. Both players move the checkers in the opposite direction to end in the home quadrat or the home board. A checker can be moved only to an open point not occupied by any player, point occupied with own checkers or a point occupied by a single checker by the opponent. Moreover, a player can place as many checkers as needed on a single point.
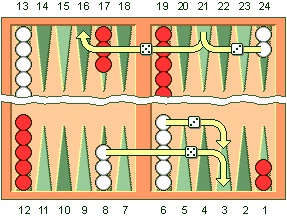
Each number of the dice can be played by a separate checker, or a single one can play the total sum of the dice numbers, but only if the intermediate point is available. For example, if a player rolls 6 and 5, one checker can be moved for 6 points towards the home board and another for 5 points. This total number of 11 moves can also be played by using only a single checker if the final point is available for that play.
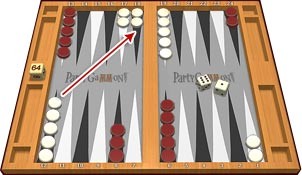
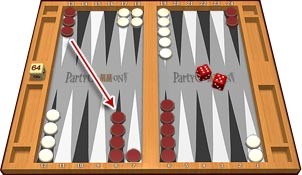
When doubles are rolled, the player needs to play the current dice numbers twice. For example, a roll of 3 and 3 means that the player has to play four 3’s (4x3) and this can be done by using 4 different checkers or less if that is a better movement strategy for the player.
After a player rolls the dice, both numbers must be played or all four if doubles are rolled. In a situation when only one number can be played, but not both, the player cannot choose which one to play, but must play the higher number. When doubles are rolled, if a player cannot play all four movements, then must play as much of the dice as possible. If none of the numbers can be played or only one, then the player losses the turn.
Hitting and entering
The protection of a point is made only by placing at least two checkers on a single point, one on top of another. This point is called blocked or a secured point and the opponent cannot use it, because it is occupied by the player. When only a single checker of either color is placed on a point, it is called a blot. Blots are unsecured points which means that not only the player can use this point, but also the opponent.

Any time the opponent lends a checker on a blot, there is a hit and the blot checker is placed on top of the bar.
(For example, Player 2 who is playing with black checkers is hitting the opponent’s white blot and that checker is placed on top of the bar. Player 1 cannot continue playing until the hit checkers are returned to the game.)
PRIMER spored slika
SLIKA za butkanje na pull
Any time a player has one or more hit checkers on the bar, the first requirement is to enter back these checkers into the opponent’s home board so he/she can continue with the game. A player cannot move any of the checkers on the board until all of the hit checkers are returned into the game. The first six opponent’s point numbers are used when a player needs to enter a hit checker into the game. Corresponding to the numbers of the rolled dice, the checker that was hit can be placed onto an open point, point already occupied with own checkers or a point on which there is only a single checker of the opponent (blot).
SLIKA za vrakjanje pul vo igra, koj point koj broj go ima
PRIMER spored slika
(For example, Player 1 rolls the dice and now have two available open points where can place the checker that was previously hit. It is up to the player to choose which point to use as a landing spot.)
If there is not an open point for entering a hit checker into the game, the player loses the turn to the opponent. Furthermore, if a player is able to enter some but not all of the checkers, the rest of them can be returned into the game within the next rolls, if available. Finally, when all the checkers from the bar are placed on the opponent’s home board, the player can continue moving the checkers on the board according to the unused numbers of the dice.
If all the points in the opponent’s home board are occupied by the opponent, than the player cannot enter a hit checker until at least one point becomes free.
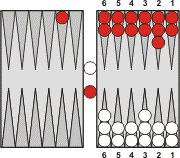
The situation when all the entering points are occupied by the opponent is called prime, and it is a huge disadvantage for a player, because he/she is not able to do anything until there is at least one single open point in the opponent’s home board. In the meantime, while the player is “on pause”, the opponent is making rolls and rapidly progressing by moving the checkers towards the home.
Bearing Off
A player is allowed to start bearing off the checkers when all fifteen are placed into the player’s home board. Since each point has a specific number starting from one to six, the player bears off the checkers from the points that corresponds to the numbers of the dice.
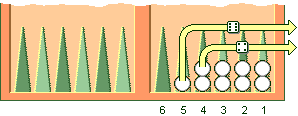
For example, if the dice are 2 and 4, it means that the player has to bear off one checker from point number 2 and one checker from point number 4.
On the other hand, if there are no checkers on the point(s) that corresponds to the dice numbers, then the player has two options. The first one is to move a checker from a higher-numbered point to a lower-numbered point, since this is the only available way. Moreover the player is under no obligation at any given time to bear off checkers if there is a possible legal move. Therefore, it is up to the player to choose what the play.
SLIKA za koga mora da se mrda pull, ako nema za vadenje
For example, if all the checkers are placed on points one, two, three and six, then if the roll is 4 and 5, the player cannot bear off, since there are not any checkers on these points, but needs to play (move) the checkers placed on the sixth point to a lower-numbered point.
Furthermore, if a player rolls the dice and get numbers that are bigger than the highest-numbered point on which checkers reside, a player is allowed to bear off checkers from that point.
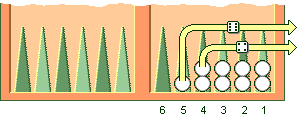
For example, if a player rolls 5 and 6, but all checkers are placed on the points from one to four, the player can bear off checkers starting from the highest point which in this case is number four.
If a checker is hit during the bearing off, the player cannot continue the process until that checker is returned to the home board.
Scoring
The player who bears off the checkers first, wins the game and gets the value of the current number of the doubling cube.
If the player bears off all the checkers before the opponent has borne off at least a single one, it corresponds to a gammon win and the winner takes twice the value of the doubling cube.
If the player bears off all the checkers and the opponent has left at least one checker in the winner’s home board or on the bar, it corresponds to a backgammon win and the winner takes three times the value of the doubling cube.
Doubling cube
Before the game starts, the two players agree on the stake and the availability of using the doubling cube during the game. This doubling cube is not just a regular die, but a special one with variables that change the original stake set prior the game. It has 6 sides, each one with a different number of 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64. At the beginning of the game this doubling cube is placed in the middle of the left bar, and afterwards it changes the location on the bar according to the player who is using it. When the game starts, the initial number of the cube is 64, which means the winner wins the original stake negotiated between the players. If the win is a gammon than the winning is double the original stake, or if it is a backgammon win, then the prize for the player is three times the initial original stake.
What the doubling cube offers, is speeding up the game when playing a match or multiplying the original stake when playing a single game. During the course of the game, when a player feels that has a sufficient advantage against the opponent, may propose a double of the stake. The first initial doubling is 2 or twice the originally set up stake. This can be done only at the start of the own turn or before the dice are rolled. In a situation like this, the opponent must either accept the doubled stake or automatically resigns the game with the current stake. Whenever a player accepts the offer, the doubling cube is moved to his/hers side of the board with the new number (stake multiplier) facing up. Furthermore, only the player that owns the doubling cube is able to make a re-double. This re-doubling between the players can switch at most six times or reaching the maximum number of 64. On the other hand, when a player rejects a doubling offer, loses the game with the value of the current stake.
For example when player 1 doubles the cube and player 2 accepts the offer, the doubling cube with a side of number two facing up is moved to the player’s 2 side. Next time when player 2 doubles the cube and player 1 accepts, the cube is moved to the player’s 1 side with the corresponding number of 4. If the original stake prior to the game was $10, now it will be $40, because of the current value of the doubling cube.
SLIKA za primerot – 2te dupliranja
But if player 1 rejects the offer, then loses the game with the current stake which would be $20 or the original stake multiplied by the current number of the doubling cube of 2.
In a match play using the doubling cube can really speed up the tempo of the game. For example if the match play is set to a length of 5 wins, then two doublings of the cube sets a total win of four games. This means that player wins 4 games automatically if the doubling cube is currently 4. All other rules for using the doubling cube in a single game, apply for a match game too.
Only under the following conditions the players can double the stake:
- The doubling cube is allowed during the rules negotiation for the game
- The game limit is set higher than the original stake
- The auto-roll function is disabled
- The doubling cube is in the middle of the board, not used by any player
- The doubling cube is on your side.
- When Crawford's rule is not applied.
Backgammon tips
Backgammon is considered to be a strategic game, with so many moves available for every single roll of the dice. Even if the player is an expert or just starting out, no one can be fully prepared for every single situation. Since the dice represent the luck factor in the game, there are so many possibilities how these two numbers can be played. But whether to use offensive or defensive strategy in combination with the dice is totally up to the player and the right choice takes the player step ahead of the opponent.
This is a list of very useful tips that will help you to become a better player and guide you what to do in situations when the dice are not on your side or options you have are not so friendly.
- Always try to make as much blocks as possible across the board. This effective strategy by moving the checkers in blocks (pairs) towards the home and not leaving blots, protect you from being hit. You can also use this strategy to get back in the game if you are behind in the race.
- In Backgammon making blocks is always a useful thing, but more important is choosing the best (crucial) points on which you are going to place them. Early in the game you should do as much as you can to control the points number five, four and seven (in that specific order), on your side and on your opponent’s side. Never let your opponent to take control of both these important strategic positions. By doing this on your side, you can easily make a prime within the next rolls which gives you the opportunity for blocking your opponent’s runners from leaving your home board. Occupying these points on your opponent’s side, gives you more options when moving your runners or entering potentially hit checkers without leaving blots.
- The best way to slow down your opponent and gain progress advantage over him/her is to create a prime. If you manage to block six consecutive points on your side of the board, then you can very easily restrict the moves of your opponent, since he/she won’t be able to pass that block and that puts you in a strong position to win. Therefore always try to trap your opponent’s runners behind a prime if the situations allows that. Easiest way is to use points seven, six, five, four and any other two before or after these.
- At the early stage of the game, rolled dice with a number difference of two, are commonly used for building blocks in the home board. Usually rolls with numbers 3 and 1, 4 and 2, 5 and 3, as well as 6 and 4, are used for making block points. In addition to blocking, home board points or blocks are also particularly important for slowing down your opponent when reentering checkers after being hit. In addition to these combinations, a very powerful roll is 6 and 1, and these numbers can be played for creating a block on point number seven.
- Always try to create advanced anchors in the early stage of the game. By doing this you can afford yourself an easier movement, while creating more difficulties at the same time for your opponent when bringing the checkers home. Your opponent's point number 5 is your best defense point. Finally, by creating advanced anchors you will not allow your opponent to make a prime and gain a huge advantage over you.
- Never forget your runners inside the opponent’s home board. One of the most important things that should be done earlier in the game is moving them out of your opponent’s home. More you wait, less options you have for playing them later in the game, since your opponent can build many block or even a prime.
- When moving the checkers towards your home, always try to equally spread them across the board, instead of building “towers” or “candlesticks”. Otherwise by doing this, you limit your game options.
- When you are way behind your opponent and he/she starts bearing off, while you still have checkers outside your home board, you should use the dice numbers wisely to avoid a gammon or backgammon win. In order to do so, you should calculate your steps carefully and bring as many checkers as possible into your home board. It means, try making crossovers whenever possible, even knowing the cost of placing all of them on point number six. In situations like this you shouldn’t worry about the non-proportional placement of the checker inside the home board, but saving a gammon or backgammon defeat.
- When you start bearing off, if your opponent still has checkers inside your home board, you should be very careful how to play the rolls. It means, if the dice allow you to bear off two checkers, but at the same time indirectly forcing you to leave a blot or two, then you should consider making moves instead of bearing off checkers, or bearing off just one checker and play another one. Being hit by your opponent in the home board can really regress your game.
- The best time to split your runners (the two checkers on point #24) is in the early stage of the game before the opponent has a chance to occupy any of his/hers home points.
- If you have a choice between hitting a checker residing on your opponent’s home or outer board, or making a block inside your home or outer board, usually a better choice is to make a hit, since your opponent will have additional pip counts for playing.
- If you are not sure what to choose between making a block or making a hit when there is a very good chance of a counter hit (re-hit), better option is to build a block or a point.
- Do not build too many blocks with only two checkers. Although building blocks is a good strategy, points with no extra checkers for playing can sometimes force you to leave blots in the later parts of the game.
- If your opponent has a few checkers inside your home board, try to make blocks instead of hitting the blots. Too many opponent’s checkers residing in your home board might strengthen your opponent’s back game instead of giving you an advantage over him/her.
- If you don’t have an available move for playing without leaving a blot at the same time, you should consider leaving a blot in your opponent’s home or outer board rather than on your side of the board, especially in the home quadrant.
- When moving a checker out of your opponent's home board, try to get it as near as possible to your opponent's point number twelve. Placing a checker on opponent’s points seven and nine should be avoided, as they make the blot too easy to hit.
- Try to leave at least 7 points distance between your blot and your opponent’s closest checker. This will force your opponent to use both dice if he/she wants to hit your blot.
- When your roll forces you to leave blots, move your second checker as close as possible to the first one. This way, your checkers will be evenly distributed and you will have more options for moving the checkers within the next rolls.
- When leaving blots, try to have other checkers located nearby (it is preferred a maximum of 6 pips away) for protection. That way, you will have the opportunity to cover the blot on your next turn, or to re-hit, if the rival dares hitting your checker.
- Be careful of leaving blots when your opponent’s home board is significantly blocked. Any hit would possibly means wasting more rolls than needed for entering the checker(s) back into the game.
- If you are already noticeably behind in the race it may not hurt your chances to fall even further behind. In a situation like this, sometimes is even better to leave a blot on purpose and being hit, which will strengthen your backgame, without breaking your inner board. But more important is to make as many blocks as possible inside your home board. This strategy will delay your opponent’s progress and hopefully turn the backgammon game in your favor if you manage to hit a checker.
- When you are moving checkers inside your home board, always try to place them equally on all six points. Creating candlesticks (usually on point five and six) can slower the process of bearing off, since you are not going to roll the numbers five and six every single time. This means, instead of bearing off checker with every roll, you will be forced to move checkers as well.
- Never hesitate to hit your opponent if you think that it will give you an advantage during the game, but try to avoid this aggressive strategy if you have blots inside your home board. If you hit a checker and next round you get hit by the opponent, then you more lose than you actually win from this situation.
- When you start bearing off, if there are opponent’s checkers inside your home board, avoid leaving an odd number of checkers on highest-numbered points, so you will not be forced to expose checkers (leave blots) when rolling high doubles like 6 and 6, 5 and 5, etc. For that reason, when bearing off try to have an even number of checkers on you highest points.
- When breaking a point and leaving a blot, it is preferable that the blot will be in danger of an indirect hit, rather than a direct hit. It means that the opponent will need the sum of both dice in order to hit, instead of using just a single die.
- Always rush when bearing off. If you are racing with your opponent in bearing off checkers, then avoid wasting your rolls. It means that if the dice allow you to bear off checkers, don't waste the roll for moving checkers forward. Therefore the most important thing in this process is to use all the dice numbers for bearing off checkers rather than trying to smooth your distribution by filling empty points.
- Pay attention to the pip counts. Since this counter tracks how many points you are left to win the game, if you see that you are way behind your opponent (your number is higher), then you should start playing more aggressively. Don’t create blocks, anchors or try landing checkers equally on all points, just focus on moving the checkers as fast as possible inside your home board.
- If your opponent offers you a resign, but you are way too ahead in the game, refuse the offer, and try to win a gammon or backgammon, which will double or triple the doubling cube. If you accept the resign, then you get just a single win.
- Anytime you are forced to play a back game, it is a good strategy to block your opponent’s points two and three. By doing this you will make it very difficult for your opponent to move the checkers inside the home board.
- When you are ahead in the race, then race. Make sure to break contact from any opposing checker and take maximum advantage of your huge lead. After all, let’s not forget the main goal which is bearing the checkers first and winning the game.
- Whenever you have an opportunity to hit, but you are unsure, just make the hit. Hitting gives your opponent additional pip counts for playing, especially if the hit is made in his/hers side of the board.
- When your opponent is ahead in the race, it is preferred to block opponent’s points seven and nine, in order to be able to defend yourself. On the other hand, these two positions also allow you to threaten opposing checkers.
- If you play a match without using the Crawford rule and your opponent is way ahead in the game, fell free to offer or accept a double. This strategy is very helpful when your opponent is only one point away from winning the match. By doing this you just increase your chances to catch the score or even win the match. For example, if the score is 4-2 in your opponent’s favor, you should offer a double, or if your opponent offer you, then accept and immediately make a redouble. What you will achieve by this is getting a chance to win the match, which would not be the case with a normal win. On the other hand, if you lose the game, it doesn’t really matter, since your opponent needs just a single point for winning the match.
- Using a safe strategy by not leaving blots is sometimes not so useful compared to other concepts such as having many flexible positions and (available) checkers ready for making blocks. Don’t hesitate to take any chances early in the game if it improves your prospects of establishing a good position very quickly.
- At the early stages in the game try to avoid putting your checkers at low points, because by doing that you will have less choices later on. For that reason you should think of other alternatives first and if not available then return to this one.
- One of the most strategic points you should block or keep (by default you have five checkers on it when the game starts), is your point number 13. It is very important for protecting your outer board and blocking the opponent’s.
- Anytime your opponent is offering you a double, and your chances for a win are less than 25%, consider rejecting the offer and losing the current stake, instead of possibly accepting the offer and losing double the stake.
- The right moment for making a doubling offer is when your chances for a win are between 60 and 70%. If you try to double when the chances for a win are slim, it might be harmful for you, since you don’t have an advantage over your opponent, just hoping to win. On the other hand if it is too obvious that you are going to win, then it is probably too late for a doubling offer, since your opponent will most probably reject it.
- Watching skilled players playing backgammon online is an excellent way to learn new backgammon strategies and upgrade your knowledge of the game.
- Sometimes the luck can be a problem if you don’t know how to use it properly. Don't get over excited when you get a lot of huge rolls and doubles in a game. Make sure you always find the best possible move and don’t let your excitement get the best out of you.
- Finally, it is all about matchups. Sometimes you can be much more skilled and experienced than your opponent, but still lose at the end, no matter how many times you play against each other. As any other game, same is with backgammon, there are many different strategies and styles of playing. Maybe your style just doesn’t produce results against your opponent’s style. In situations like this there is only one solution. Change your style and try to use other strategies and moves that you normally don’t use.







